Abstract
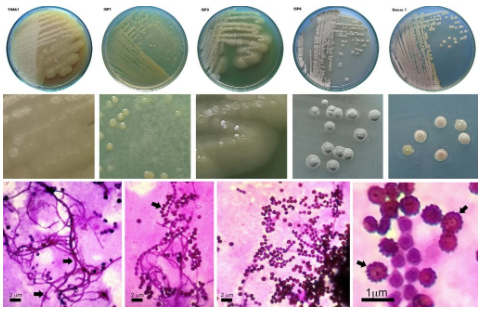
In view that Actinobacteria produce various types of potential antibiotics and enzymes for pharmaceutical industry, some Actinobacteria strains were isolated from the soil samples collected around tree roots in Ho Chi Minh City and Binh Duong province and further screened for the desired bioactivities. After drying at 60 °C for 30 minutes, these soil samples were diluted and spreaded on Gause 1 agar. Forty-seven Actinobacteria strains were isolated. Of these 24/47 (51%) demonstrated antimicrobial activities. The potential KD33 strain was analyzed in term of morphological, biochemical, and antimicrobial characteristics. Antimicrobial activity of the isolated bacteria was identified by the agar plug diffusion method to detect the antagonism against the tested microorganisms including Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 43300, Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212, Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853, Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 35657 and Candida albicans ATCC 10231. The ethyl acetate-crude-extracts of the KD33 strain cultured in 7 days were analyzed by TLC-bioautography. Notably, KD33 strain showed a significant effect on all tested bacteria. TLC-bioautography revealed two bands of evident anti- staphylococcal activities at Rf 0.07 and 0.37.